See what is is the basic principle of an optical refractometric sensor.
With reference to the following picture, by lighting a fibre optic test segment embedded within a host material, the optical signal is transmitted to the interface between the end of optical fibre and the material, where the measurement take place. At the interface, part of the light beam is refracted and part is reflected, depending on the refractive index mismatch between the fibre and the under test material.
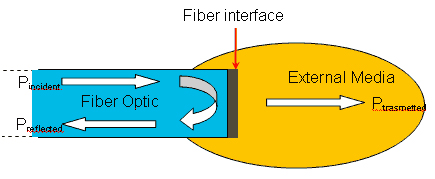
If a monomode fibre is used, the intensity reflection coefficient R can be expressed as:
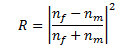
where nf and nm are respectively the effective refractive index of the fibre and the sample refractive index. Any change involving host refractive index variation results in an amplitude modulation of the reflected signal.
On the fiber interface can be deposited a selective-substance-absorbing polymer thin layer to increase the sensor features in terms of selectivity and sensitivity.
That kind of sensors is able to monitor the phenomena which cause the variation of the thickness and refractive index of the polymeric film. This principle is usually used in the chemical sensing.
